Comp 303 Final Notes
For more notes on design patterns, see here
UML
Unified Modeling Language
Object Diagram
For class instances
- Cards are labelled with
name:type - Values may be primitives or references pointing to other cards
Class Diagram
For static, compile-time view
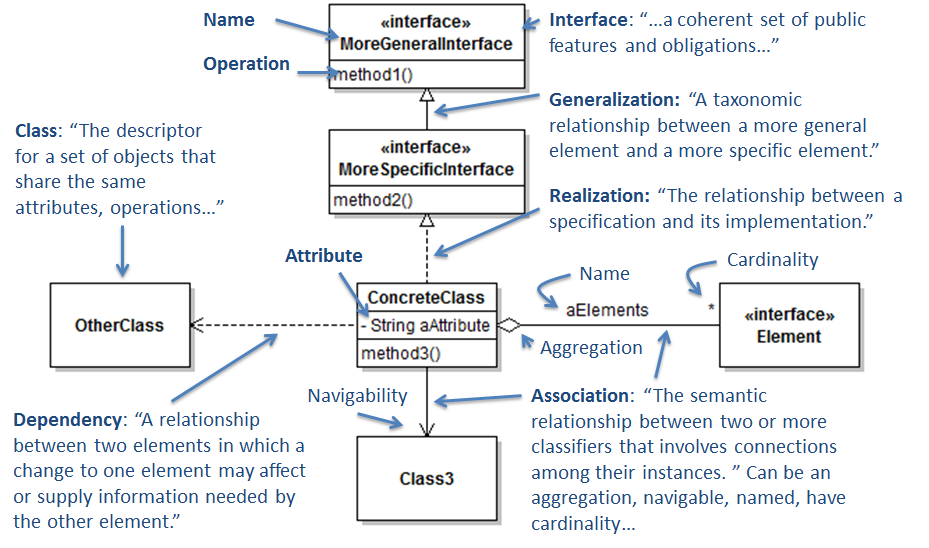
Taken from prmr/SoftwareDesign
| Label | Basic Meaning |
|---|---|
| Generalization | extend |
| Realization | implements |
| Dependency | change in one will change another |
| Association | general relationship (eg fields); bi-directional if no arrow drawn |
| Aggregation | “has a/many” associative relationship |
| Composition | physical aggregation (typically, item in composition cannot exist without parent class) |
Note that:
- Diamond is on the side of the container for aggregation/composition
- Aggregation/composition should indicate cardinality (eg
2,0..52, etc) - Elements represented through arrows should not be duplicated within the cards
State Diagram
For dynamic, run-time view
- Start denoted by black dot
- End denoted by black dot with circle
- States represented by cards
- Arrows denote transitions
- Annotated as
name[condition] | action(only name is mandatory)
- Annotated as
- Lack of transition means that it is invalid
Concurrency
try {
lock.lock(); //Reentrant Lock
// do stuff
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// handle stuff
return; // finally will still be called
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
Serialization
public class Data {
private String name;
private int count;
private String value;
/**
* @param name must not have a space
* @param count
* @param value must not have a space
*/
public Data(String name, int count, String value) {
this.name = name;
this.count = count;
this.value = value;
}
public static Data deserialize(String data) {
if (data.charAt(0) != '"' || data.charAt(data.length() - 1) != '"')
throw new IllegalArgumentException("data not in serialized form");
String[] parts = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1).split(" ");
return new Data(parts[0], Integer.parseInt(parts[1]), parts[2]);
}
public String serialize() {
return String.format("\"%s %d %s\"", name, count, value);
}
public static void write(String path, Data... data) throws IOException {
try (PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(path))) {
for (Data d : data)
out.println(d.serialize());
}
}
public static Data[] read(String path) throws IOException {
List<Data> data = new ArrayList<>();
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path))) {
for (String line = in.readLine(); line != null; line = in.readLine())
data.add(Data.deserialize(line));
}
Data[] result = new Data[data.size()];
data.toArray(result);
return result;
}
}
